Signal Authentication Service
The Cabinet Office has developed a signal authentication service that can confirm whether a signal received by a GNSS receiver is actually a signal transmitted from a positioning satellite or not. The service started in April 2024.
Vulnerability of the Positioning Signal
Since the specifications of the civil signals broadcast by GNSS satellites are open to the public, it is possible for a third party with knowledge to produce the same positioning signals. However, until now, there has been no mechanism to distinguish between positioning signals generated by third parties and positioning signals from GNSS satellites.
In recent years, "spoofing" that exploits the security vulnerability of positioning signals has become a social issue in satellite positioning.
If a GNSS receiver without spoofing countermeasures is attacked, for example, it can be recognized as if it is in Kanagawa Prefecture on the data, even though it is actually in Tokyo. Therefore, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with autonomous flight functions, vehicles with autonomous driving functions, and autonomous navigation vessels may be hijacked.
Overview of Signal Authentication Service
This service uses digital signature authentication technology to provide a mechanism for verifying the authenticity of positioning signals.
Specifically, the QZSS control station generates digital signature data using the private key. The digital signature data is included it in the positioning signal information (navigation message), and it is distributed it via the QZSS.
The user (GNSS receiver) verifies whether or not the navigation message has been tampered by performing arithmetic processing using the public key obtained in advance, the received digital signature data, and the navigation message (hash value).This makes it possible to confirm that the positioning signal is authentic.
This mechanism enables users to perform secure positioning using only positioning signals transmitted from real positioning satellites.
In addition to control and safety support for automatic driving, etc., possible fields of application for this service include movement records (digital tachographs, car navigation systems, navigation information recorders, etc.) and time servers.
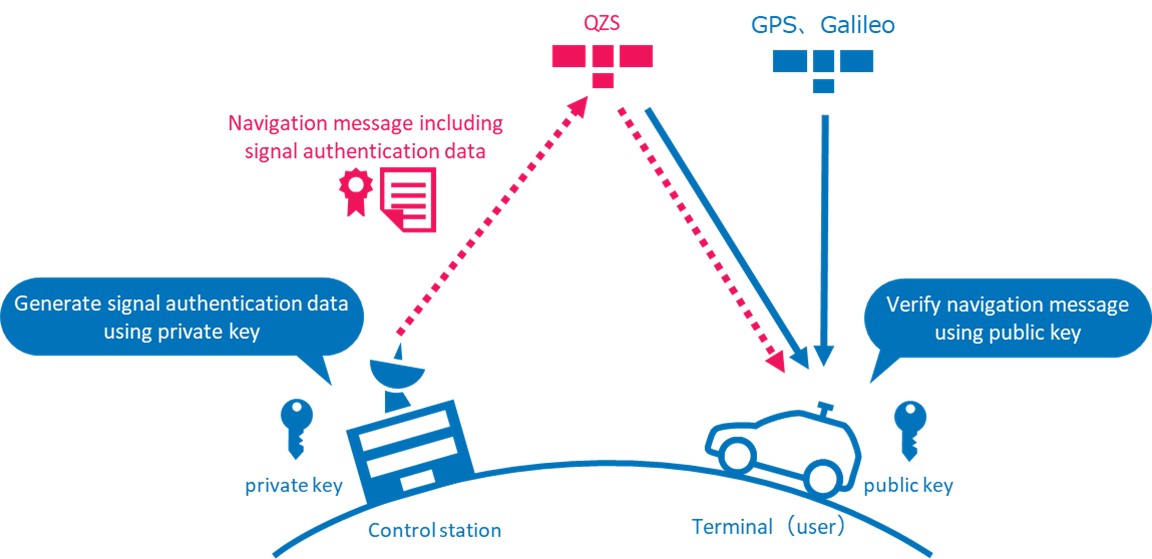
Image of Signal Authentication Service
*1: The signal authentication data using the key for testing will be transmitted. The test transmission may be cancelled or interrupted depending on circumstances.
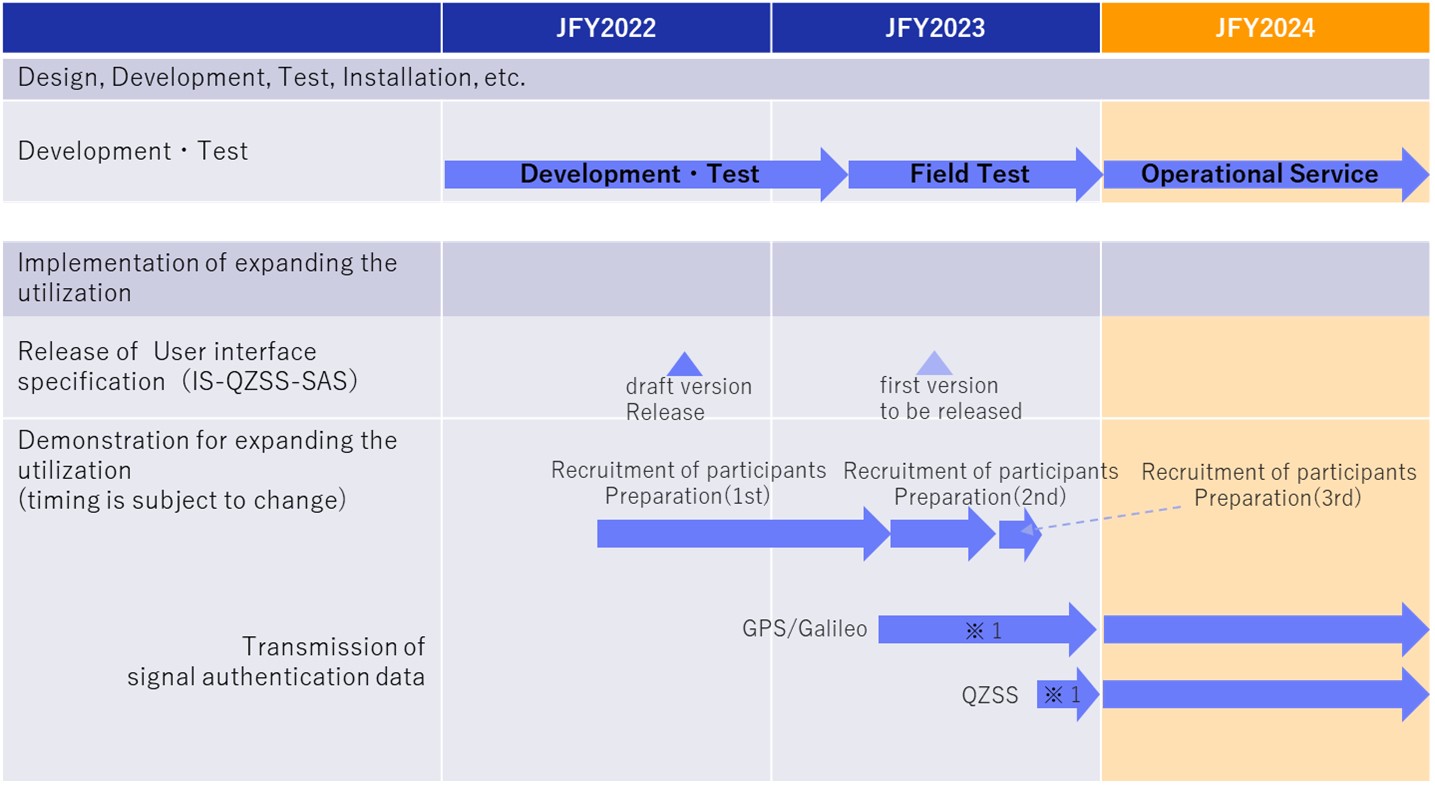
Schedule (JFY: April to March)
Public Keys
Since the signal authentication data provided by this service includes a digital signature generated with a private key based on public key cryptography, a GNSS receiver should have the corresponding public key in advance to use this service to verify the authenticity of the positioning signal.
The public key required for this service will be distributed to each user such as vendors who wish to use the signal authentication service. Specific application and distribution methods will be announced on the MICHIBIKI WEB at a later date.

Image of public key distribution
-

Overview of the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
-

What is the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)?
-

QZSS is Becoming a Seven-satellite Constellation
-

Advantages of QZSS
-

Service Comparison
-

Transmission Signals
-

Satellite Positioning, Navigation and Timing Service (PNT)
-

Sub-meter Level Augmentation Service (SLAS)
-

Centimeter Level Augmentation Service (CLAS)
-

Multi-GNSS Advanced Orbit and Clock Augmentation - Precise Point Positioning (MADOCA-PPP)
-

Satellite Report for Disaster and Crisis Management (DC Report)
-

QZSS Safety Confirmation Service (Q-ANPI)
-

Positioning Technology Verification Service
-

Public Regulated Service
-

SBAS Transmission Service


