Overview of the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
QZSS is a Japanese satellite positioning system composed mainly of satellites in quasi-zenith orbits (QZO). However, the term “Quasi-Zenith Satellite (QZS)” can refer to both satellites in QZO and geostationary orbits (GEO). For that reason, the name “QZO satellite” is used when it is necessary to specifically refer to satellites in QZO.
Satellite positioning systems use satellite signals to calculate position information. One famous example is the American Global Positioning System (GPS); the QZSS is sometimes called the “Japanese GPS.”
Complements GPS for satellite positioning, navigation and timing service that is more precise and stable
Satellite positioning is possible with four or more satellites, but a larger number of satellites is ideal for obtaining stable positioning information. However, the number of visible GPS satellites was smaller in urban and mountainous areas where satellite signals are obstructed by buildings, trees, and other objects, making the stable acquisition of positioning information impossible in some cases.
QZSS (Michibiki) has been operated as a four-satellite constellation from November 2018, and three satellites are visible at all times from locations in the Asia-Oceania region. QZSS can be used in an integrated way with GPS, ensuring a sufficient number of satellites for stable, high-precision positioning. QZS are compatible with GPS and receivers can be procured at a low cost, so it is expected that position information businesses utilizing geographical and spatial information will be developed.
-

What is the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)?
-
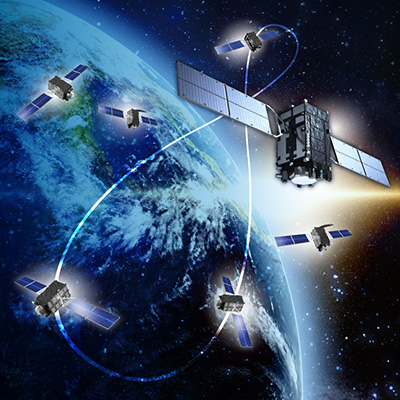

QZSS is Becoming a Seven-satellite Constellation
-

Advantages of QZSS
-

Service Comparison
-

Transmission Signals
-

Satellite Positioning, Navigation and Timing Service (PNT)
-

Sub-meter Level Augmentation Service (SLAS)
-

Centimeter Level Augmentation Service (CLAS)
-

Multi-GNSS Advanced Orbit and Clock Augmentation - Precise Point Positioning (MADOCA-PPP)
-

Satellite Report for Disaster and Crisis Management (DC Report)
-

QZSS Safety Confirmation Service (Q-ANPI)
-

Positioning Technology Verification Service
-

Signal Authentication Service
-

Public Regulated Service
-

SBAS Transmission Service


