Advantages of QZSS
In recent years more countries are developing and establishing original satellite positioning systems. However, QZSS is superior to these systems. As many countries launch positioning satellites, only Japan's QZSS is highly compatible with GPS and can be used with GPS in an integrated way; QZSS and GPS can be utilized as a single group of satellites. To put it simply, with QZSS it is like the number of GPS satellites has been increased. Because QZSS can be used in an integrated way with GPS, the number of satellites that can transmit satellite signals at the same time is increased, which makes highly precise, stable positioning possible. This also decreases the positioning errors as described.
[Reference] The Modernization of GPS
When GPS satellites reach the end of their life span, failures can occur and the satellites are put out of service at times. Therefore, replacement GPS satellites are launched in a systematic way. When new satellites are launched, the old satellites are replaced with new-model GPS satellites with the goal of improving positioning capabilities.
The currently launched satellites are second-generation Block IIF series satellites that transmit L5 signals.
Seven second-generation Block IIA satellites - which offer poor positioning accuracy compared to the new models - are being operated, but they are being sequentially replaced with new-model satellites. The current GPS error, which is said to be 0.8 meters, will be improved to 0.4 meters by 2018, thereby drastically improving the positioning environment.
| L1C/A | L1C | L2C | L5 | Error | 2014 | 2018 | 2020 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single frequency | II A | ◎ | One – two meters | Eight satellites | |||||
| II R | ◎ | 0.5 meters | 12 satellites | 10 satellites | Six satellites | ||||
| Dual frequency or multiple frequency |
II RM | ◎ | ◎ | 0.5 meters | Seven satellites | Seven satellites | Seven satellites | ||
| II F | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.3 meters | Five satellites | 12 satellites | 12 satellites | ||
| III | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | 0.3 meters | Two satellites | Six satellites | ||
| Total 32 satellites | Total 31 satellites | Total 31 satellites | |||||||
* "Error" is defined as an error in the satellite position transmitted by a standalone satellite.
-

Overview of the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
-

What is the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)?
-

QZSS is Becoming a Seven-satellite Constellation
-

Service Comparison
-

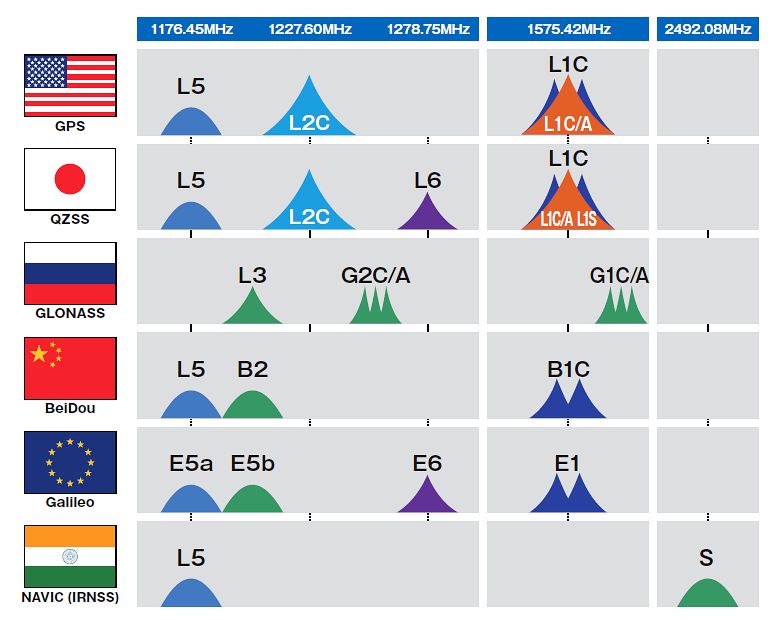
Transmission Signals
-

Satellite Positioning, Navigation and Timing Service (PNT)
-

Sub-meter Level Augmentation Service (SLAS)
-

Centimeter Level Augmentation Service (CLAS)
-

Multi-GNSS Advanced Orbit and Clock Augmentation - Precise Point Positioning (MADOCA-PPP)
-

Satellite Report for Disaster and Crisis Management (DC Report)
-

QZSS Safety Confirmation Service (Q-ANPI)
-

Positioning Technology Verification Service
-

Signal Authentication Service
-

Public Regulated Service
-

SBAS Transmission Service


