-
Previous
Sub-meter Level Augmentation Service (SLAS)

-
Next
Multi-GNSS Advanced Orbit and Clock Augmentation - Precise Point Positioning (MADOCA-PPP)

Centimeter Level Augmentation Service (CLAS)
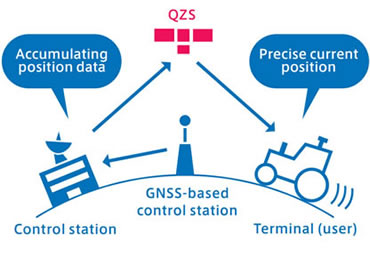
To carry out highly precise satellite positioning, distances from the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan's GNSS-based control stations are calculated using data from these control stations. Information used to accurately search for one's current position (centimeter level augmentation information) is transmitted by QZS. L6D signals that send centimeter level augmentation information are not transmitted by GPS, so dedicated receivers are required.
It is expected that this service will be used for surveying, intelligent construction (construction methods in which construction machinery is operated with high precision), and e-agriculture (methods for agricultural land management in which agricultural machinery is operated with high precision). It This service can be used on L6D signal receivers. In addition, because it employs a method using the positioning technology of carrier wave positioning, larger antennas and receivers are used. Accordingly, it is expected that this service will be used for surveying and on-board vehicle equipment as well as mobile devices.
With centimeter level augmentation, positioning can be accomplished with an error of several centimeters by utilizing surveying technologies. If the longitude and latitude coordinate system that serves as the standard was a national datum built via surveying with old technologies, it is not always the case that this system will have a high degree of accuracy. However, high-precision augmentation can be accomplished with geocentric coordinates. Consequently, for utilization of this service in on-site surveying, control surveying of Level 3 or 4 control point surveys and photographic surveys are currently being considered.
This service can also be used in three-dimensional measuring systems in which cameras and laser scanners are installed on vehicles together with receivers. By obtaining high-precision positions and image information on the ground, it is expected that accurate maps can be created more promptly.
Because this takes place via satellites, there is a time lag of between 10 and 20 seconds until the augmentation information is created and transmitted. The augmentation may not take place in time, and positioning results may be negatively impacted, in cases such as sudden ionospheric disturbance. For that reason, when using this service in vehicles it is expected that utilization will be limited to certain areas such as plant sites and farms, or post-processing will be used like three-dimensional measuring. For driving on public roads, this service will be utilized in an auxiliary way.

-

Overview of the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
-

What is the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)?
-

QZSS is Becoming a Seven-satellite Constellation
-

Advantages of QZSS
-

Service Comparison
-

Transmission Signals
-

Satellite Positioning, Navigation and Timing Service (PNT)
-

Sub-meter Level Augmentation Service (SLAS)
-

Multi-GNSS Advanced Orbit and Clock Augmentation - Precise Point Positioning (MADOCA-PPP)
-

Satellite Report for Disaster and Crisis Management (DC Report)
-

QZSS Safety Confirmation Service (Q-ANPI)
-

Positioning Technology Verification Service
-

Signal Authentication Service
-

Public Regulated Service
-

SBAS Transmission Service


